总体方法一览
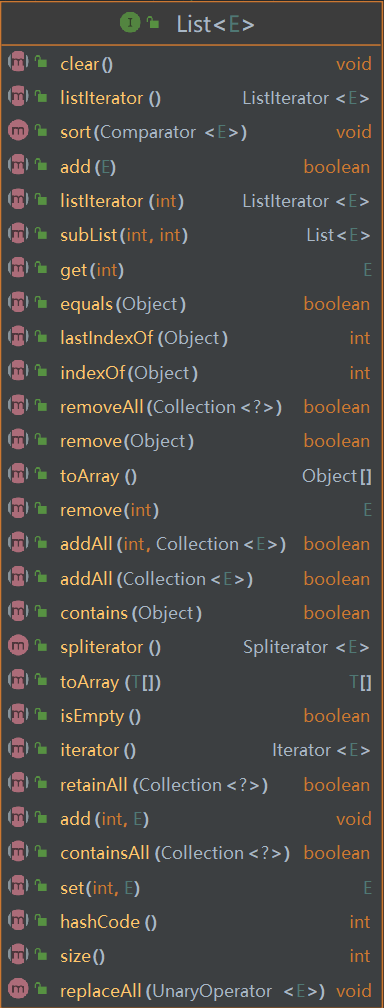
说明
由于List接口继承自Collection接口,因此部分方法已经在讲Collection接口方法时讲过了,这里只讲一下List接口特有的方法
请参考:Collection接口方法详解
以下方法均以ArrayList为例作演示,其他List接口实现类可以参考以下方法的用法
1
| List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
|
add
List接口在Collection接口的基础上重载了一个add方法
- void add(int index , E element)
该方法可以在指定索引index位置插入元素element,其他元素则向后移动一位,下标索引从0开始
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(0);
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(1, 6);
System.out.println(arrayList);
|
get
可以使用索引来取得对应位置的元素,下标索引从0开始
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
System.out.println(arrayList.get(1));
System.out.println(arrayList.get(3));
|
set
可以修改指定索引index的元素element
返回该索引元素修改之前的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
System.out.println(arrayList.set(2, 8));
System.out.println(arrayList);
|
remove
List接口在Collection接口的基础上重载了一个remove方法
可以删除指定索引位置index的元素
返回值为删除的元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
System.out.println(arrayList);
System.out.println(arrayList.remove(1));
System.out.println(arrayList);
|
addAll
List接口在Collection接口的基础上重载了一个add方法
- boolean addAll(int index, E element)
可以从指定索引位置开始,将一个集合(这里称为集合B)中的所有元素插入到另一个集合(这里称为集合A)中去
插入成功返回true,插入失败返回false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
List<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> B = new ArrayList<>();
A.add(0);
A.add(1);
A.add(2);
A.add(3);
B.add(8);
B.add(8);
B.add(8);
System.out.println(A.addAll(2, B));
System.out.println(A);
System.out.println(B);
|
indexOf
查找List集合指定元素element第一次出现的位置
找到则返回第一次出现的位置索引,没有找到则返回-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
List<Integer> C = new ArrayList<>();
C.add(1);
C.add(1);
C.add(2);
C.add(2);
System.out.println(C.indexOf(1));
System.out.println(C.indexOf(2));
System.out.println(C.indexOf(3));
|
lastIndexOf
查找List集合指定元素element最后一次出现的位置
找到则返回最后一次出现的位置索引,没有找到则返回-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
System.out.println(C.lastIndexOf(1));
System.out.println(C.lastIndexOf(2));
System.out.println(C.lastIndexOf(3));
|
subList
从List集合中指定位置[fromIndex,toIndex)返回一个List子集合
List<E> subList(fromIndex, toIndex)
注意:这个List子集合和List集合是绑定在一起的,会相互影响,即subList返回的是List的一个视图
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
List<Integer> subListC = C.subList(1, 3);
System.out.println("C: " + C);
System.out.println("subListC: " + subListC);
subListC.set(0, 9);
System.out.println("subListC: index = 0, element: 1->9");
System.out.println("C: " + C);
System.out.println("subListC: " + subListC);
C.set(2, 9);
System.out.println("C: index = 2, element: 2->9");
System.out.println("C: " + C);
System.out.println("subListC: " + subListC);
|
listIterator
返回一个listIterator迭代器,这个迭代器比Lterator更加强大,可以双向移动,且方法更多
有两个重载函数
-
ListIterator listIterator()
返回一个默认迭代器,初始位置指定索引为0的位置
-
ListIterator listIterator(int index)
返回一个初始位置指定索引为index位置的迭代器
1
2
3
4
|
ListIterator<Integer> it = C.listIterator();
ListIterator<Integer> it1 = C.listIterator(1);
|













